PostgreSQL Change Data Capture (CDC) overview
Change Data Capture Extraction
Data Integration Change Data Capture (CDC) extraction mode provides a real-time stream of any changes made to the databases and tables configured, eliminating the need to implement and maintain incremental fields or retrieve data via select queries. It also enables you to retrieve deleted rows and schema changes from the database.
The Change Data Capture (CDC) mechanism is based on a Write-Ahead Log (WAL) provided by the PostgreSQL database. The logical decoding feature of PostgreSQL is available in versions 10 and higher.
In PostgreSQL, the logical decoding mechanism creates a consistent and easy-to-understand format in a single location. The logical decoding mechanism in PostgreSQL is based on converting the data written to the WAL using an output plugin that converts the WAL transaction rows into a dedicated format. To consume data from the database, you must install the output plugin on the PostgreSQL server and enable the logical decoding configuration. For more information on setting up a PostgreSQL database for Data Integration CDC extraction, refer to the PostgreSQL configuration documentation.
Data Integration offers CDC extraction mode for PostgreSQL on both Google Cloud SQL and Amazon RDS / Aurora.
Data Integration uses the output plugin to continuously pull new rows in the WAL to pull data using the CDC architecture. To get historical data from the database, Data Integration cannot rely on the entire log history existing before setting up a river. PostgreSQL typically maintains a record of the WAL and purges it after a specified period.
Data Integration uses the Overwrite loading mode to create a complete snapshot (or migration) of the chosen table(s) to align the data and metadata as it was on the first run. After the migration is complete, Data Integration takes the existing WAL records and performs an Upsert-merge to the target table(s), while continuing to fetch new records from the log as they are created.
Data Integration PostgreSQL connector reads WAL records and generates change events in the FileZone files for row-level INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE commands. Each file represents a set of database operations performed over a period of time. The data from the log is continuously streamed into the FileZone path determined by the river (with timeframes of no more than 15 minutes) and pushed into the target according to the river's scheduled frequency. This method saves the data first in the File Zone, and then it can be moved into the target DWH at any time.
For more information on File Zone, refer to the Target topic.
CDC Point in Time position feature
The CDC "Point in Time" Position feature provides deeper insights into the operational details of a River's streaming process. This feature is essential for data recovery and synchronization, enabling you to locate and retrieve data from a specific point in history using the exact information stored in the CDC log position. For more information, refer to documentation.
A sequence change data capture deployment
Discrepancies in transaction records can occur when two users simultaneously execute identical transactions, resulting in conflicts in the timestamp field. Data Integration implemented a "sequence" Change Data Capture (CDC) mechanism to tackle this issue.
Data Integration enhanced each emitted record from the database by incorporating two extra metadata fields: '__transaction_id' and '__transaction_order'.
-
The '__transaction_id' field serves as a unique identifier for each transaction, ensuring that no two transactions share the same identifier. This uniqueness enables precise identification and differentiation between transactions, thereby mitigating conflicts that arise from identical timestamps.
-
The '__transaction_order' field denotes the order in which the transactions were emitted from the database. By incorporating this field, the sequencing of transactions can be accurately maintained, enabling downstream systems such as Apache Kafka or AWS Kinesis to process and order transactions correctly.
Including these metadata fields ensures that the ordering of transactions is preserved throughout the River, letting smooth and accurate transaction flows be achieved and resolving discrepancies that previously arose from transactions with identical timestamps.
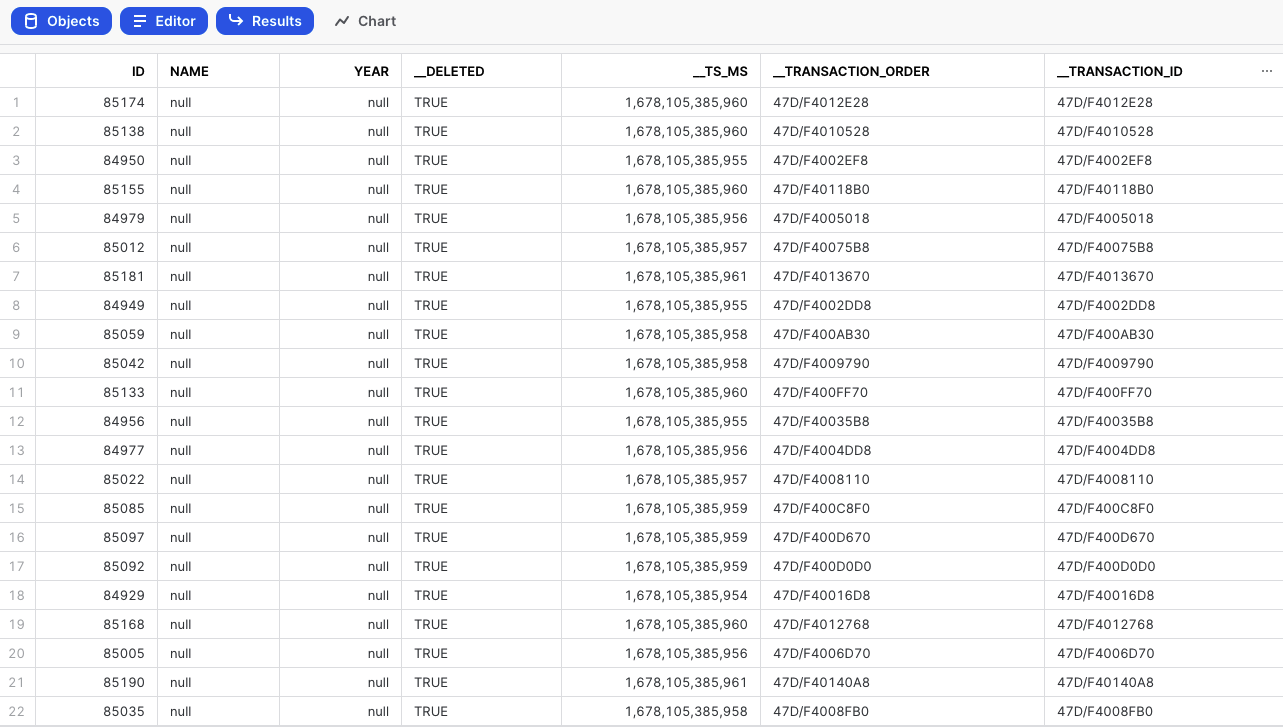
For further information about Change Data Capture (CDC) Metadata Fields, refer to our Database Overview document.
Partitioned tables in PostgreSQL
Data Integration supports PostgreSQL partitioned tables in both Standard Extraction and Change Data Capture (CDC).
For PostgreSQL versions 13 and later, partitioned tables can be replicated using logical replication. For more details on logical replication limitations, refer to PostgreSQL's documentation.
Configuring logical replication for partitioned tables
To enable logical replication, you must create a publication for your tables. Publications provide selective replication; you can add or remove tables dynamically. Only tables included in a publication are replicated to Data Integration. Each database can have multiple distinct publications.
Steps to create a publication
- Ensure you have CREATE privileges or higher.
- Create a publication for all tables using the following command:
CREATE PUBLICATION data_integration_pub FOR ALL TABLES WITH (publish_via_partition_root=true);
The publication name 'data_integration_pub' is provided as an example. The actual publication name must be unique for each database and cannot start with a number.
Partitioning method support
Data Integration supports only declarative partitioning using '_CREATE TABLE ... _PARTITION B Y' command. This approach is necessary for accurate change tracking in PostgreSQL versions 13 and later.
Legacy inheritance-based partitioning is not supported.
Troubleshooting
Verifying logical replication
Before enabling CDC Streaming in Data Integration, verify that logical replication is working correctly by running the following query:
FROM pg_logical_slot_peek_binary_changes('data_integration_slot', null, null, 'proto_version', '1', 'publication_names', 'data_integration_pub');```
If CDC streaming is already enabled on a River that reads from the same slot, the query fails with the following error:
```ERROR: replication slot "data_integration_slot" is active for PID 12345```
To resolve this issue:
* Disable CDC streaming on the relevant River.
* Re-run the query to verify replication.
## Enable Change Data Capture extraction
After establishing a [connection](../Connections/connection-postgresql.md), go to the Source tab to enable Change Data Capture extraction.
## Procedure
1. Navigate to the [{conKeyRefs.DataIntegration} Account](https://console.rivery.io/).
2. Select the river or create one, and then choose the connection that you created.
3. Go to the **Source** tab.
4. Choose the **Multi-Tables** as the River mode.
5. Select the **Log Based** as the extraction mode.<!---->
6. Check your connection and set up your **Source and Target**. Select 'Got It' to proceed.
7. Choose Log-Based Version from the **Advanced Options** drop-down menu.
8. Set the name of the [**custom replication slot**](../SetupGuides/configuring-replication-slots-and-publications#custom-replication-slots) (optional).
9. Set a [**custom publication name**](../SetupGuides/configuring-replication-slots-and-publications#publication-slots-configuration) (optional).
10. Turn the **Enable Log** toggle to true at the bottom of the page. <!---->
11. Select **Target**. <!---->
<!-- 12. You'll be directly sent to the Target tab, where you can choose your data target. -->
12. Define your Target connection, then choose a Database and a Schema to load into.
13. To make sure the operation is complete, click the **Enable Log** toggle once more. <!---->
14. Click **Schema** to navigate to the Schema tab.
15. Click **Show Me My Schemas**. <!---->
A minimum of one Schema must be chosen.
16. To use CDC, the table must contain a key, which is defined as the Source Column - id. <!---->
17. Navigate to the **Enable Log** toggle and select the number of hours you want to run the River, then click **I'm Sure**. <!---->
- Wait for the Initiation Log to complete its processing. <!---->
- You are all set to run your log-based River now. Following the completion of the River Run, return to the Schema tab and check that the selected Table is **Streaming**. <!---->
## Type mapping in CDC
While extracting your data, the system matches PostgreSQL data types to {conKeyRefs.DataIntegration} data types.
The mapping of PostgreSQL data types to {conKeyRefs.DataIntegration}-compatible types:
**PostgreSQL Type**| **{conKeyRefs.DataIntegration} Type**
---|---
BOOLEAN| BOOLEAN
BYTEA| STRING
TOAST| -Not Supported-
CHAR| STRING
VARCHAR| STRING
TEXT| STRING
JSON| JSON
JSONB| JSON
DATE| STRING
FLOAT4| STRING
FLOAT8| STRING
INT2| INTEGER
INT4| INTEGER
INT8| INTEGER
INTERVAL| STRING
NUMERIC| FLOAT
TIME| STRING
TIMESTAMP| STRING
TIMESTAMPTZ| STRING
UUID| STRING
XML| STRING
## Limitations
* The 'TOAST' file format is not supported.
* Any special character is replaced with an underscore. As a result, if you want to edit the table name, go to:
1. The 'Schema' tab
2. Select a Table
3. Click 'Table Settings.'
4. Choose 'Edit' to change the table name manually. <!---->
## Current stream position in your database
To confirm the Stream position, run the following command on the server:
SELECT pg_current_wal_lsn() - '0/0' AS lsn_position;
